Scabies and Personal Hygiene

Scabies is a very contagious type of skin disorder caused by infestation with microscopic mites. The parasite mite that causes scabies in humans is called Sarcoptes scabiei var. hominis. This type of parasitic organism is the only scabies mite that can complete its life cycle on the bodies of human hosts. Although animal mites can also cause temporary allergic reactions to people, they are unable to infest humans.
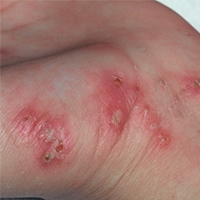
The majority of symptoms generated by scabies occur as a consequence of allergic reactions to the mites’ secretions and eggs. The mites feed on human blood and they contaminate the skin with their bites, releasing substances that are toxic to the human body. Once they burrow within the epidermis, scabies mites cause inflammation, rashes and itch.
If scabies is not discovered in time, the mite infestation can generate serious symptoms such as skin lesions and ulcerations, formation of crust, painful nodules, blisters and pustules. The skin regions affected by scabies are very vulnerable to bacterial infections and some patients also develop skin disorders such as impetigo.
There are many misconceptions and unfunded ideas regarding scabies. Due to the high incidence of scabies among people from lower classes of society, one would be tempted to believe that scabies is the result of inappropriate hygiene and unhealthy lifestyle. In fact, the level of hygiene doesn’t really influence the occurrence or the development of scabies. Recent studies have revealed the fact that good personal hygiene can’t effectively prevent infestation with scabies mites.
At best, proper hygiene can only delay the occurrence of scabies and its generated symptoms.
The actual reason for the high incidence of scabies in less developed urban societies is overcrowding. Scabies is very contagious and it can be easily transmitted through direct physical contact. Thus, living in overcrowded conditions facilitates the spreading of scabies from one family member to another.
Scabies epidemics are very common in overcrowded orphanages, kindergartens, schools and hospitals. During scabies outbreaks, everyone should follow an appropriate treatment in order to prevent the occurrence of the disease.
Scabies mites can live for several days in the absence of a human host. Within this period of time, the parasitic scabies mites can easily infest bed sheets, towels, clothes and various personal items.
Although scabies is rarely acquired indirectly, doctors strongly recommend washing any items that may be contaminated with scabies mites.
Scabies continues to be contagious even on the duration of the medical treatment. As a precaution, people affected by scabies should avoid entering in close contact with other persons until they complete the treatment prescribed by a dermatologist. When the symptoms of scabies persist for more than a week after the treatment, it is a possible sign of re-infestation with mites. If the doctor finds new traces of mite infestation, the treatment for scabies should be repeated.